The human population is continuously exposed to ionizing radiation from several natural sources that can be classified in two categories:
- Cosmic contribution: high-energy cosmic rays incident on the Earth's atmosphere and releasing secondary radiation
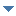
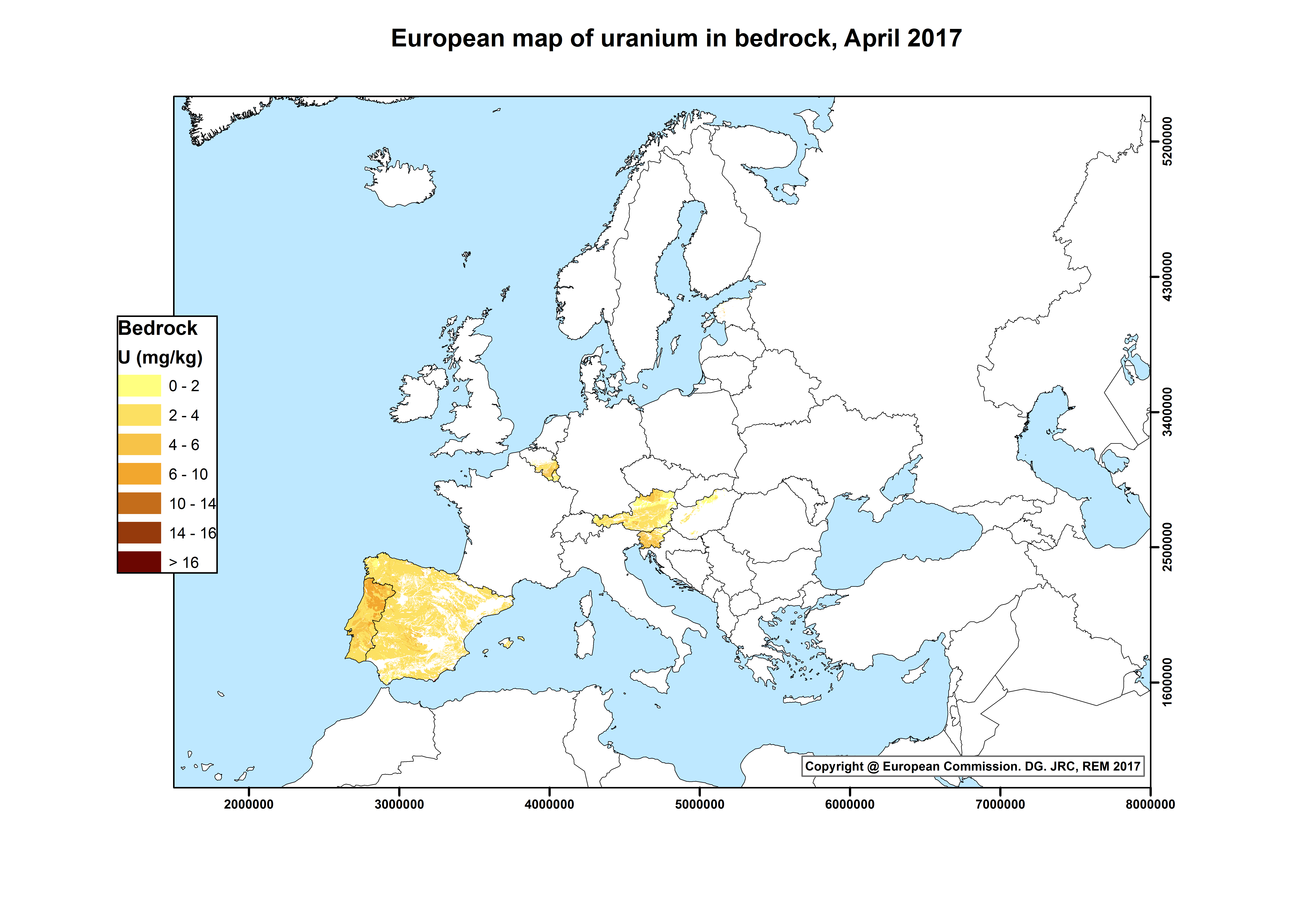
- Terrestrial contribution: radioactive nuclides generated during the formation of the Earth and still present in the Earth's crust: mostly uranium and thorium radioactive families together with potassium (40K), which is a long-lived radioactive isotope of the elemental potassium. In most circumstances radon, a noble gas produced in the radioactive decay of the Uranium progeny, is the major contributor to the total dose.
The European Atlas of Natural Radiation is a collection of maps displaying the levels of radioactivity caused by different natural sources in Europe.
The Atlas is intended to familiarise the public with the radioactive environment, to give a more balanced view of the annual dose that it may receive from natural radioactivity and to provide reference material and generate harmonised data for the scientific community. The overall goal of the Atlas is to estimate the annual dose that the public may receive from natural radioactivity, combining all the information from the different maps. Indeed, natural ionizing radiation is considered the largest contributor to the collective effective dose received by the world population.
The Atlas is developed and maintained by the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission.